Manguezal 937: Protecting a Vital Mangrove Ecosystem
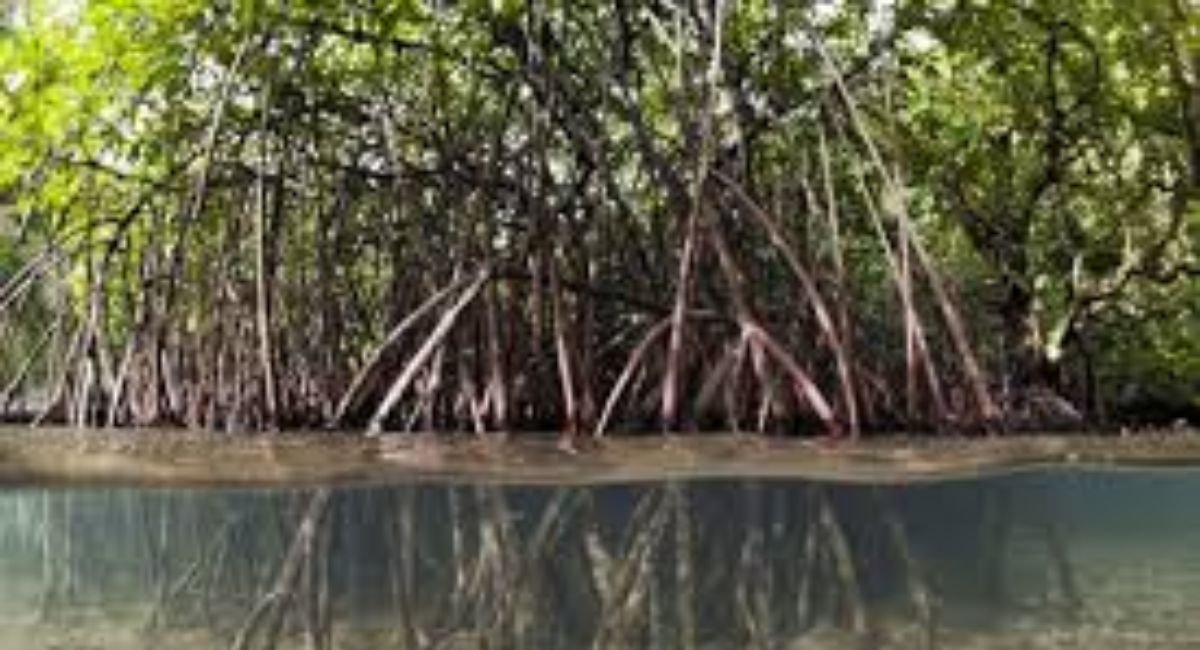

Mangroves are often called the “rainforests of the sea” due to their crucial role in supporting biodiversity, protecting coastal areas, and mitigating climate change. Among these ecosystems, Manguezal 937 stands out as a significant area that demands attention for its environmental importance and the challenges it faces. Located in a region rich in biodiversity, Manguezal 937 is not just a sanctuary for numerous species but also a vital line of defense against rising sea levels and coastal erosion.
In this article, we will explore the ecological importance of Manguezal 937, the threats it faces, the role of mangrove forests in global ecosystems, and the efforts being made to restore and protect these fragile environments. By understanding the critical role of Manguezal 937, we can better appreciate the need for its conservation and how it contributes to the health of our planet.
What is Manguezal 937?
Manguezal 937 refers to a specific mangrove ecosystem located along a coastal region that is notable for its diverse array of plant and animal life. Mangroves, including Manguezal 937, are unique ecosystems typically found in tropical and subtropical regions. They are characterized by salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that grow in intertidal zones, where the land meets the sea.
Manguezal 937 is especially significant due to its role as a breeding ground for marine life, including fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. These mangrove forests serve as a natural buffer, protecting coastlines from erosion caused by storms and rising sea levels. Additionally, they act as carbon sinks, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide and thus playing a role in mitigating climate change.
In many ways, Manguezal 937 serves as a microcosm of the larger global mangrove ecosystems, illustrating the intricate balance between land and sea, and the profound impact these areas have on both local and global environmental health.
Ecological Importance of Manguezal 937
The ecological importance of Manguezal 937 cannot be overstated. This mangrove ecosystem is a haven for a wide range of species, including fish, birds, reptiles, and mammals. Many species depend on this habitat for shelter, food, and breeding grounds, making it a biodiversity hotspot.
Biodiversity Support
Mangrove ecosystems like Manguezal 937 are home to a vast number of species, some of which are endangered or endemic to the region. The tangled roots of mangrove trees create a safe environment for juvenile fish, crabs, and other marine organisms. This not only supports local fisheries but also ensures the survival of species that are critical to the health of marine food chains.
Bird species, including migratory birds, also rely on mangroves for nesting and feeding. Manguezal 937 acts as a crucial stopover for many migratory species, offering a rich source of food and protection during long journeys.
Coastal Protection
One of the most important roles of Manguezal 937 is its ability to protect coastlines. The dense root systems of mangrove trees help stabilize shorelines by reducing the impact of waves and preventing erosion. This is especially vital in areas prone to hurricanes, typhoons, and other severe weather events.
In addition to reducing erosion, Manguezal 937 serves as a natural barrier against storm surges, protecting coastal communities from flooding. As sea levels rise due to climate change, the importance of preserving these natural defenses becomes even more apparent.
Carbon Sequestration
Mangroves are among the most efficient carbon sinks in the world, meaning they can absorb and store large amounts of carbon dioxide. Manguezal 937 plays a significant role in this process, helping to mitigate the effects of global climate change. The dense vegetation and organic matter found in mangrove forests trap carbon within their soils, preventing it from being released into the atmosphere.
In fact, it is estimated that mangroves can sequester up to four times more carbon than other types of tropical forests. This makes them essential tools in the global fight against climate change, and underscores the importance of protecting and restoring ecosystems like Manguezal 937.
Threats Facing Manguezal 937
Despite its importance, Manguezal 937 faces numerous threats that jeopardize its survival and the well-being of the species that depend on it. Human activities, climate change, and pollution have all contributed to the degradation of mangrove ecosystems worldwide, and Manguezal 937 is no exception.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
One of the most pressing threats to Manguezal 937 is deforestation, often driven by urban development, agriculture, and aquaculture. In many coastal regions, mangroves are cleared to make way for shrimp farms or other forms of commercial development. This leads to the destruction of crucial habitats and undermines the natural services that mangroves provide, such as coastal protection and carbon sequestration.
Once mangroves are removed, the land often becomes more vulnerable to erosion, leading to a loss of soil and increased vulnerability to storms. Deforestation of mangroves also disrupts the delicate balance of the ecosystem, leading to the displacement or death of species that depend on these habitats.
Climate Change and Rising Sea Levels
Climate change is another major threat to Manguezal 937. Rising sea levels and increased temperatures pose a significant challenge to mangrove ecosystems, as they depend on specific conditions to thrive. As sea levels rise, mangroves may struggle to keep pace, leading to the loss of critical habitat areas.
Moreover, higher temperatures can lead to changes in the composition of mangrove forests, affecting species that have adapted to specific environmental conditions. This can result in reduced biodiversity and the loss of species that are not able to adapt to the new conditions.
Pollution and Water Quality
Mangroves like Manguezal 937 are also highly susceptible to pollution, particularly from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and plastic debris. Pollution can degrade water quality, leading to the death of marine life and the decline of plant species that form the foundation of the ecosystem.
In particular, oil spills and chemical pollutants can have devastating effects on mangrove ecosystems. These pollutants can suffocate the roots of mangrove trees, causing widespread death and destruction within the forest.
Conservation and Restoration Efforts for Manguezal 937
Recognizing the ecological importance of Manguezal 937, conservationists, governments, and local communities have begun taking steps to protect and restore this valuable ecosystem. Mangrove restoration is a growing focus in global environmental efforts, and there are several strategies being employed to safeguard Manguezal 937.
Reforestation Initiatives
One of the most effective ways to restore mangroves is through reforestation efforts. By planting new mangrove trees and rehabilitating degraded areas, conservationists can help rebuild the ecosystem and restore its natural functions. In Manguezal 937, reforestation initiatives are underway to expand the mangrove coverage and promote the recovery of damaged areas.
Local communities are often involved in these initiatives, as they have a vested interest in the health of the mangroves. Community-led restoration programs not only benefit the environment but also provide economic opportunities, such as ecotourism and sustainable fisheries.
Legal Protections and Regulations
To prevent further destruction, governments and environmental organizations are working to implement stronger legal protections for mangrove ecosystems. In many regions, mangroves are designated as protected areas, limiting development and restricting activities that could harm the environment. These legal measures are critical in ensuring the long-term survival of Manguezal 937.
Enforcing these regulations, however, remains a challenge. Continued efforts are needed to monitor and protect mangrove ecosystems from illegal deforestation and other harmful activities.
Sustainable Development Practices
Promoting sustainable development practices is key to balancing economic growth with environmental conservation. In coastal regions near Manguezal 937, there is a growing focus on sustainable agriculture, aquaculture, and urban development that minimizes harm to the environment. By adopting practices that reduce pollution, conserve water, and protect natural habitats, it is possible to support both the local economy and the health of the mangrove ecosystem.
The Role of Manguezal 937 in Global Environmental Health
The protection of Manguezal 937 is not just a local concern but a global one. As one of the world’s most efficient carbon sinks, mangroves play a critical role in reducing greenhouse gases and mitigating the effects of climate change. Additionally, by preserving biodiversity and supporting local fisheries, mangroves contribute to food security and the livelihoods of millions of people worldwide.
Manguezal 937 serves as a prime example of how interconnected ecosystems are, and how protecting one area can have far-reaching impacts on global environmental health. As awareness of the importance of mangrove ecosystems grows, so too does the urgency of protecting and restoring areas like Manguezal 937.
FAQs
What makes Manguezal 937 important for biodiversity?
Manguezal 937 is home to numerous species of fish, birds, and other wildlife that rely on the mangroves for breeding, shelter, and feeding. Its biodiversity supports local ecosystems and contributes to the global marine environment.
How do mangroves protect against coastal erosion?
Mangrove root systems help stabilize shorelines by reducing the force of waves and holding soil in place. This reduces coastal erosion and protects communities from storm surges and flooding.
What are the main threats to Manguezal 937?
The main threats to Manguezal 937 include deforestation, climate change, rising sea levels, and pollution from agricultural and industrial activities.
Can mangrove ecosystems recover from damage?
Yes, with proper restoration efforts, including reforestation and sustainable management practices, mangrove ecosystems like Manguezal 937 can recover and continue providing environmental benefits.
How does Manguezal 937 contribute to combating climate change?
Mangroves, including Manguezal 937, are highly effective carbon sinks, absorbing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide, which helps mitigate global warming.
What can individuals do to help protect mangroves?
Individuals can help by supporting conservation initiatives, reducing plastic waste, and promoting sustainable practices that reduce pollution and deforestation near mangrove ecosystems.
Conclusion
The protection and restoration of Manguezal 937 are critical for safeguarding biodiversity, protecting coastal communities, and combating climate change. This unique mangrove ecosystem offers a wealth of environmental benefits, from supporting marine life to acting as a natural barrier against rising sea levels. Through conservation efforts, sustainable development, and community involvement, we can ensure that Manguezal 937 continues to thrive for generations to come.